Doing good thanks!  Hope you are well too!
Hope you are well too!
We have completed the initial work on making this technically work and now bug fixing and some other improvements that came from quality control such as adding to the installer and making the configuration simpler.
I believe the documentation and script are in a good place. Below are the current PowerShell options and manual guide that will make it to the docs when we release this. Please let me know if you think I am missing anything!
Create and Export Certificate (For EntraID Certificate Authentication rather than client secret)
# Create Self-Signed Certificate for use with Entra App Registration for dev environments.
$Name = "PingCastle-Email"
$password = "ENTER PASSWORD"
# Create a self-signed certificate
$cert = New-SelfSignedCertificate -Subject "CN=PingCastle-Email" -CertStoreLocation "Cert:\LocalMachine\My" -KeyExportPolicy Exportable
# Create a password for the PFX
$pwd = ConvertTo-SecureString -String $password -Force -AsPlainText
# Export the certificate as PFX
Export-PfxCertificate -Cert $cert -FilePath "$env:USERPROFILE\$Name.pfx" -Password $pwd
# Export the certificate as CER for Entra
Export-Certificate -Cert $cert -FilePath "$env:USERPROFILE\PingCastle-Email.cer" -Type CERT
Write-Output "Certificate exported to: $env:USERPROFILE\$Name.pfx"
Email Creation Function
<#
.SYNOPSIS
Advanced PowerShell function to automate RBAC for Applications setup in Exchange Online
.DESCRIPTION
This function automates the complete process of creating an Azure AD app registration,
shared mailbox, and configuring RBAC for Applications in Exchange Online.
Specifically designed for PingCastle-Email configuration.
.PARAMETER TenantId
The Azure AD tenant identifier (GUID) where the application and service principal will be created.
.PARAMETER ClientSecretExpiration
The lifetime of the client secret in months. Defaults to 12.
.PARAMETER SharedMailboxDomain
The SMTP domain portion for the new shared mailbox (e.g. “contoso.com”).
.PARAMETER CertificateAuth
Switch to enable certificate-based authentication instead of client secret.
.PARAMETER CertificatePath
File system path to the certificate (PFX) to use when CertificateAuth is enabled.
.PARAMETER AppName
The display name of the Azure AD application to create. Defaults to “PingCastle-Email”.
.PARAMETER ServicePrincipalName
The name of the service principal for the application. Defaults to “PingCastle-Email”.
.PARAMETER ManagementScopeName
The name of the custom role scope to assign to the service principal. Defaults to “PingCastle-Email”.
.PARAMETER SharedMailboxName
The local part of the shared mailbox alias. Defaults to “pingcastle-email”.
.PARAMETER SharedMailboxDisplayName
The display name for the shared mailbox. Defaults to “PingCastle-Email”.
.EXAMPLE
Set-PingCastleEmailRBAC -TenantId "your-tenant-id"
.EXAMPLE
Set-PingCastleEmailRBAC -TenantId "your-tenant-id" -CertificateAuth -CertificatePath "C:\Certs\pingcastle.pfx"
.NOTES
Author: Joe Dibley
Version: 1.0
Requires: Exchange Online Management Module, Microsoft Graph PowerShell Module
#>
function Set-PingCastleEmailRBAC {
[CmdletBinding()]
param(
[Parameter(Mandatory = $true)]
[string] $TenantId,
[Parameter(Mandatory = $false)]
[int] $ClientSecretExpiration = 12,
[Parameter(Mandatory = $true)]
[string] $SharedMailboxDomain,
[Parameter(Mandatory = $false)]
[switch] $CertificateAuth,
[Parameter(Mandatory = $false)]
[string] $CertificatePath,
[Parameter(Mandatory = $false)]
[string] $AppName = "PingCastle-Email",
[Parameter(Mandatory = $false)]
[string] $ServicePrincipalName = "PingCastle-Email",
[Parameter(Mandatory = $false)]
[string] $ManagementScopeName = "PingCastle-Email-Scope",
[Parameter(Mandatory = $false)]
[string] $SharedMailboxName = "pingcastle-Email",
[Parameter(Mandatory = $false)]
[string] $SharedMailboxDisplayName = "PingCastle-Email"
)
$SharedMailboxAddress = "$SharedMailboxName@$SharedMailboxDomain"
# Results object to store all configuration details
$Results = @{
Success = $false
AppRegistration = @{}
SharedMailbox = @{}
ServicePrincipal = @{}
ManagementScope = @{}
RoleAssignment = @{}
TestResults = @{}
Errors = @()
}
Write-Host "Starting PingCastle-Email RBAC Configuration..." -ForegroundColor Cyan
Write-Host "=============================================" -ForegroundColor Cyan
try {
# Step 1: Check and install required modules
Write-Host "Step 1: Checking required PowerShell modules..." -ForegroundColor Yellow
$RequiredModules = @("Microsoft.Graph.Applications", "Microsoft.Graph.Users", "ExchangeOnlineManagement")
foreach ($Module in $RequiredModules) {
if (!(Get-Module -ListAvailable -Name $Module)) {
Write-Host "Installing module: $Module" -ForegroundColor Green
Install-Module -Name $Module -Force -AllowClobber -Scope CurrentUser
}
Import-Module -Name $Module -Force
}
# Step 2: Connect to Microsoft Graph
Write-Host "Step 2: Connecting to Microsoft Graph..." -ForegroundColor Yellow
$GraphScopes = @(
"Application.ReadWrite.All",
"Directory.ReadWrite.All",
"User.ReadWrite.All"
)
Connect-MgGraph -TenantId $TenantId -Scopes $GraphScopes
# Step 3: Create Azure AD App Registration
Write-Host "Step 3: Creating Azure AD App Registration..." -ForegroundColor Yellow
$AppRegistration = New-MgApplication -DisplayName $AppName -SignInAudience "AzureADMyOrg"
if ($AppRegistration) {
Write-Host "App Registration created successfully" -ForegroundColor Green
$Results.AppRegistration = @{
ApplicationId = $AppRegistration.AppId
ObjectId = $AppRegistration.Id
DisplayName = $AppRegistration.DisplayName
}
}
# Step 4: Create Service Principal
Write-Host "Step 4: Creating Service Principal..." -ForegroundColor Yellow
$ServicePrincipal = New-MgServicePrincipal -AppId $AppRegistration.AppId
if ($ServicePrincipal) {
Write-Host "Service Principal created successfully" -ForegroundColor Green
$Results.ServicePrincipal = @{
ObjectId = $ServicePrincipal.Id
AppId = $ServicePrincipal.AppId
DisplayName = $ServicePrincipal.DisplayName
}
}
# Step 5: Create Authentication Credential
Write-Host "Step 5: Creating Authentication Credential..." -ForegroundColor Yellow
if ($CertificateAuth -and $CertificatePath) {
# Certificate-based authentication
if (Test-Path $CertificatePath) {
$Certificate = New-Object System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates.X509Certificate2($CertificatePath)
$KeyCredential = @{
Type = "AsymmetricX509Cert"
Usage = "Verify"
Key = $Certificate.RawData
}
Update-MgApplication -ApplicationId $AppRegistration.Id -KeyCredentials $KeyCredential
Write-Host "Certificate credential added" -ForegroundColor Green
$Results.AppRegistration.AuthenticationType = "Certificate"
$Results.AppRegistration.CertificateThumbprint = $Certificate.Thumbprint
} else {
throw "Certificate file not found at: $CertificatePath"
}
} else {
# Client secret authentication
$ClientSecret = Add-MgApplicationPassword -ApplicationId $AppRegistration.Id -PasswordCredential @{
DisplayName = "PingCastle-Email Secret"
EndDateTime = (Get-Date).AddMonths($ClientSecretExpiration)
}
Write-Host "Client secret created (expires in $ClientSecretExpiration months)" -ForegroundColor Green
$Results.AppRegistration.ClientSecret = $ClientSecret.SecretText
$Results.AppRegistration.SecretId = $ClientSecret.KeyId
$Results.AppRegistration.AuthenticationType = "ClientSecret"
}
# Step 6: Connect to Exchange Online
Write-Host "Step 6: Connecting to Exchange Online..." -ForegroundColor Yellow
Connect-ExchangeOnline -ShowBanner:$false
# Step 7: Create Shared Mailbox
Write-Host "Step 7: Creating Shared Mailbox..." -ForegroundColor Yellow
# Check if mailbox already exists
$ExistingMailbox = Get-Mailbox -Identity $SharedMailboxAddress -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
if (!$ExistingMailbox) {
$SharedMailbox = New-Mailbox -Shared -Name $SharedMailboxDisplayName -PrimarySmtpAddress $SharedMailboxAddress -Alias $SharedMailboxName
if ($SharedMailbox) {
Write-Host "Shared mailbox created successfully" -ForegroundColor Green
$Results.SharedMailbox = @{
DisplayName = $SharedMailbox.DisplayName
PrimarySmtpAddress = $SharedMailbox.PrimarySmtpAddress
Alias = $SharedMailbox.Alias
Created = $true
}
}
} else {
Write-Host "! Shared mailbox already exists" -ForegroundColor Yellow
$Results.SharedMailbox = @{
DisplayName = $ExistingMailbox.DisplayName
PrimarySmtpAddress = $ExistingMailbox.PrimarySmtpAddress
Alias = $ExistingMailbox.Alias
Created = $false
}
}
# Step 8: Block shared mailbox sign-in
Write-Host "Step 8: Blocking shared mailbox sign-in..." -ForegroundColor Yellow
$MailboxUser = Get-Mailbox -Identity $SharedMailboxAddress
if ($MailboxUser.ExternalDirectoryObjectId) {
Update-MgUser -UserId $MailboxUser.ExternalDirectoryObjectId -AccountEnabled:$false
Write-Host "Shared mailbox sign-in blocked" -ForegroundColor Green
}
# Step 9: Create Service Principal in Exchange Online
Write-Host "Step 9: Creating Service Principal in Exchange Online..." -ForegroundColor Yellow
$ExoServicePrincipal = New-ServicePrincipal -AppId $AppRegistration.AppId -ObjectId $ServicePrincipal.Id -DisplayName $ServicePrincipalName
if ($ExoServicePrincipal) {
Write-Host "Exchange Online Service Principal created" -ForegroundColor Green
}
# Step 10: Create Management Scope
Write-Host "Step 10: Creating Management Scope..." -ForegroundColor Yellow
$ManagementScope = New-ManagementScope -Name $ManagementScopeName -RecipientRestrictionFilter "EmailAddresses -eq '$SharedMailboxAddress'"
if ($ManagementScope) {
Write-Host "Management Scope created" -ForegroundColor Green
$Results.ManagementScope = @{
Name = $ManagementScope.Name
RecipientFilter = $ManagementScope.RecipientFilter
}
}
# Step 11: Create Role Assignment
Write-Host "Step 11: Creating Role Assignment..." -ForegroundColor Yellow
$RoleAssignment = New-ManagementRoleAssignment -Role "Application Mail.Send" -App $ServicePrincipal.Id -CustomResourceScope $ManagementScopeName
if ($RoleAssignment) {
Write-Host "Role Assignment created" -ForegroundColor Green
$Results.RoleAssignment = @{
Name = $RoleAssignment.Name
Role = $RoleAssignment.Role
RoleAssignee = $RoleAssignment.RoleAssignee
CustomResourceScope = $RoleAssignment.CustomResourceScope
}
}
# Step 12: Test Configuration
Write-Host "Step 12: Testing Configuration..." -ForegroundColor Yellow
Start-Sleep -Seconds 30 # Wait for replication
$TestResult = Test-ServicePrincipalAuthorization -Identity $ServicePrincipal.Id -Resource $SharedMailboxAddress
if ($TestResult) {
$Results.TestResults = @{
RoleName = $TestResult.RoleName
GrantedPermissions = $TestResult.GrantedPermissions
InScope = $TestResult.InScope
AllowedResourceScope = $TestResult.AllowedResourceScope
}
if ($TestResult.InScope -eq $true) {
Write-Host "Configuration test passed - Service Principal has access to shared mailbox" -ForegroundColor Green
$Results.Success = $true
} else {
Write-Host "✗ Configuration test failed - Service Principal does not have access to shared mailbox" -ForegroundColor Red
$Results.Errors += "Test failed: Service Principal not in scope for shared mailbox"
}
}
# Step 13: Display Summary
Write-Host "`n" -NoNewline
Write-Host "Configuration Summary" -ForegroundColor Cyan
Write-Host "=====================" -ForegroundColor Cyan
Write-Host "App Name: $AppName" -ForegroundColor White
Write-Host "Application ID: $($AppRegistration.AppId)" -ForegroundColor White
Write-Host "Object ID: $($ServicePrincipal.Id)" -ForegroundColor White
Write-Host "Shared Mailbox: $SharedMailboxAddress" -ForegroundColor White
Write-Host "Management Scope: $ManagementScopeName" -ForegroundColor White
Write-Host "Authentication Type: $($Results.AppRegistration.AuthenticationType)" -ForegroundColor White
if ($Results.AppRegistration.AuthenticationType -eq "ClientSecret") {
Write-Host "Client Secret: $($Results.AppRegistration.ClientSecret)" -ForegroundColor Yellow
Write-Host "WARNING: Save the client secret securely - it cannot be retrieved again!" -ForegroundColor Red
}
if ($Results.AppRegistration.AuthenticationType -eq "Certificate") {
Write-Host "Certificate Thumbprint: $($Results.AppRegistration.CertificateThumbprint)" -ForegroundColor White
}
Write-Host "`nConfiguration completed successfully!" -ForegroundColor Green
} catch {
$Results.Success = $false
$Results.Errors += $_.Exception.Message
Write-Host "Error: $($_.Exception.Message)" -ForegroundColor Red
throw
} finally {
# Disconnect from services
Disconnect-ExchangeOnline -Confirm:$false -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Disconnect-MgGraph -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
}
return $Results
}
RBAC for Applications Setup Guide: PingCastle Email Configuration
This guide provides step-by-step instructions for configuring Role Based Access Control (RBAC) for Applications in Exchange Online, specifically for the PingCastle-Email application to send emails from the shared mailbox pingcastle@stealthbitslab.com.
“PingCastle-Email” is used throughout this configuration. This is a name and can be substituted for anything.
Prerequisites
Before starting this configuration, ensure you have:
- Global Administrator or Exchange Administrator permissions
- Application Developer permissions in Azure AD
- Exchange Online PowerShell module installed or use the Cloud Management Shell.
- Microsoft Graph PowerShell module installed (optional, for advanced scenarios)
Part 1: Create Azure AD App Registration
Step 1: Access Microsoft Entra Admin Center
- Open a web browser and navigate to https://entra.microsoft.com
- Sign in with your administrator account
- If you have access to multiple tenants, use the Settings gear icon in the top menu to switch to the correct tenant
Entra admin center homepage with Settings menu highlighted
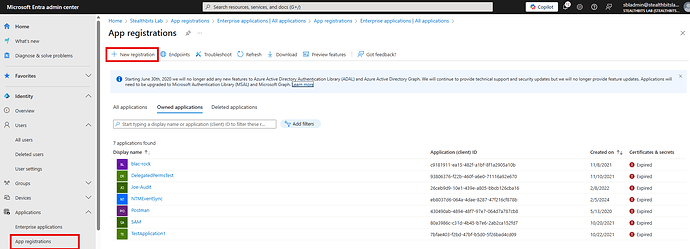
Step 2: Navigate to App Registrations
- In the left navigation pane, expand Identity
- Click on Applications
- Select App registrations
- Click + New registration at the top of the page
App registrations page with New registration button highlighted
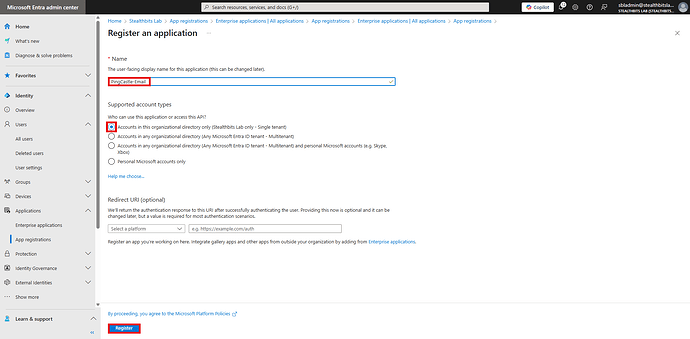
Step 3: Configure Application Registration
- In the Name field, enter:
PingCastle-Email
- Under Supported account types, select Accounts in this organizational directory only
- Leave Redirect URI (optional) blank for now
- Click Register
Register an application form with fields filled in
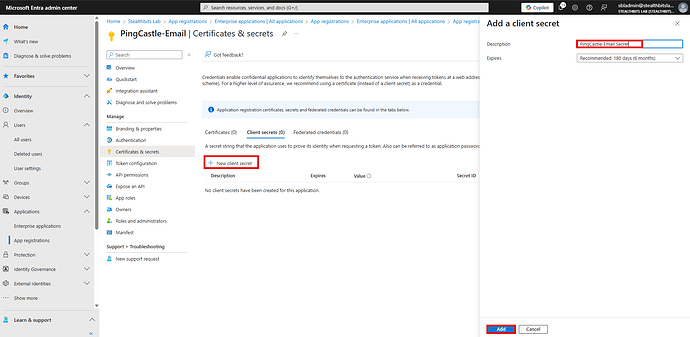
Step 4: Create Client Secret
- In the left menu under Manage, click Certificates & secrets
- Click + New client secret
- Add a description:
PingCastle-Email Secret
- Set expiration to 12 months (or as per your policy)
- Click Add
- Important: Copy the secret Value immediately - it won’t be shown again
- Paste it in Notepad or a password manager for future use in this tutorial.
If you misplace your secret you can just come back to this screen and generate a new one
Client secrets page
Part 2: Create Shared Mailbox
Step 5: Access Exchange Admin Center
- Navigate to https://admin.exchange.microsoft.com
- Sign in with your Exchange administrator account
- In the left navigation, expand Recipients
- Click Mailboxes
Exchange Admin Center navigation
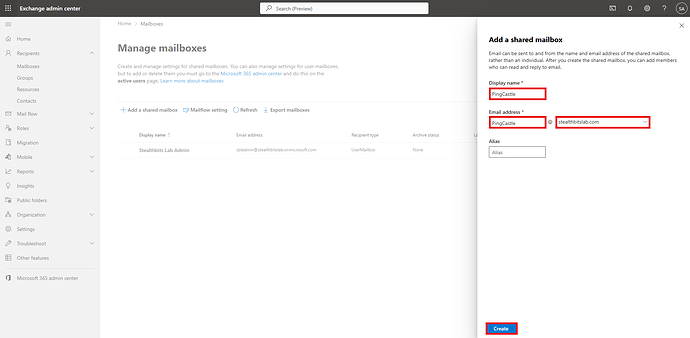
Step 6: Create Shared Mailbox
- Click + Add a shared mailbox
- Fill in the following details:
- Display Name: PingCastle
- Email Address: pingcastle (the domain should auto-populate with your domain)
- Alias: pingcastle (optional)
- Click Create
Add a shared mailbox form with fields filled
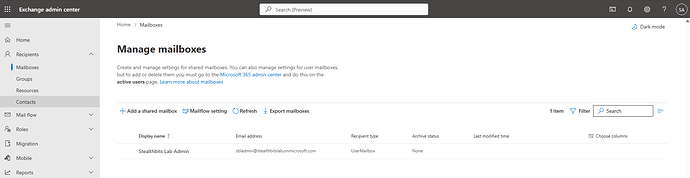
Step 7: Verify Shared Mailbox Creation
- Wait for the mailbox creation process to complete
- Verify the mailbox appears in the mailboxes list
- Note the full email address:
pingcastle@stealthbitslab.com
Mailboxes list showing the new shared mailbox
Step 8: Block Shared Mailbox Sign-in
This should automatically be completed but make sure to double check it.
- Navigate to https://entra.microsoft.com/
- Go to Users > All Users
- Search for and select the user account corresponding to the shared mailbox
- Click Edit Properties
- Click on the Settings tab
- Un-tick the Account Enabled checkbox
- Click Save
User properties page with Account Enabled set to false
Part 3: Configure RBAC for Applications
Step 9: Connect to Exchange Online PowerShell
- Open Windows PowerShell as Administrator
- Run the following commands
# Install Exchange Online Management module if not already installed
Install-Module -Name ExchangeOnlineManagement -Force -AllowClobber
# Import the module
Import-Module ExchangeOnlineManagement
# Connect to Exchange Online
Connect-ExchangeOnline
Step 10: Create Service Principal
Using the values from your app registration, create the service principal:
# Define variables (replace with your actual values)
$AppId = "YOUR_APPLICATION_CLIENT_ID"
$ObjectId = "YOUR_APPS_SERVICE_PRINCIPAL_OBJECT_ID" # Get this from the Enterprise Applications screen in Entra ID. This is not the ObjectID of your App Registration!
# Create Service Principal
New-ServicePrincipal -AppId $AppId -ObjectId $ObjectId -DisplayName "PingCastle-Email"
Step 11: Create Management Scope
Create a management scope that restricts access to only the PingCastle shared mailbox:
# Create Management Scope
$EmailAddress = "pingcastle@stealthbitslab.com" # The email address of the shared mailbox
New-ManagementScope -Name "PingCastle-Email-Scope" -RecipientRestrictionFilter "EmailAddresses -eq '$EmailAddress'"
Step 12: Assign Application Role
Assign the Application Mail.Send role to the service principal with the custom scope:
# Create Role Assignment
$ObjectId = "" # The Exchange Service Principal Object Id (This is output in Step 10)
New-ManagementRoleAssignment -Role "Application Mail.Send" -App $ObjectId -CustomResourceScope "PingCastle-Email-Scope"
Part 4: Test Configuration
Step 13: Test Service Principal Authorization
Verify the configuration works correctly:
# Test Service Principal Authorization
$EmailAddress = "pingcastle@stealthbitslab.com" # The email address of the shared mailbox
$ObjectId = "" # The Exchange Service Principal Object Id (This is output in Step 10)
Test-ServicePrincipalAuthorization -Identity $ObjectId -Resource $EmailAddress
Expected Output:
- RoleName: Application Mail.Send
- InScope: True
Step 14: Verify Scope Restriction
Test that the service principal cannot access other mailboxes:
# Test Service Principal Authorization
$EmailAddress = "" # A random email that the application should not be able to send as.
$ObjectId = "" # The Exchange Service Principal Object Id (This is output in Step 10)
Test-ServicePrincipalAuthorization -Identity $ObjectId -Resource $EmailAddress